7 Processed Foods You Should Be Eating
By Winter LeBlanc
Updated October 21, 2021
Nope… not donuts. When we hear about processed foods we tend to think of junk food like donuts and other products that are high in calories and low in nutritional value. The tricky thing about processed foods is that food processing is a spectrum. When foods are processed they undergo changes but the amount of nutrients lost in the process varies.
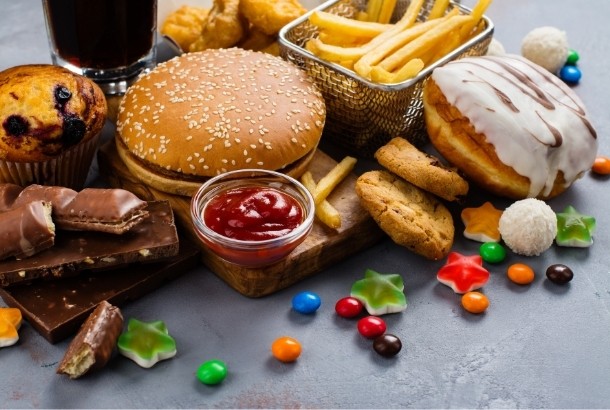

The foods in the photo above are ultra processed. Ultra processed foods are foods that go through multiple stages of processing and result in food products that are considered “industrial formulations”. These types of food products often contain added ingredients that can have negative impacts on our health such as preservatives, hydrogenated oils and refined sugars. There is evidence to suggest that consumption of ultra processed foods is associated with faster aging, heart disease, and different types of cancer.
But some foods that undergo processing are still some of the healthiest. Here are seven processed foods that you should be eating.
1. Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Not all oils are made the same. Extra virgin olive oil is a keystone of the Mediterranean Diet because of its common place in Mediterranean cuisine and remarkable cardioprotective effects. It is so healthy partly because of the way it is made.

Modern olive oil processing begins when olives are mechanically crushed within 24 hours of being harvested. The paste that is produced is then thoroughly mixed and then goes through a process of decantering that results in separation between water, oil and pomace. The oil is then mixed at high speeds, which separates the heavier liquids from the lighter liquids. The lighter liquid is the purest olive oil that is then bottled and sold. The term “extra virgin” refers to this processing practice and the fact that it does not include any chemical treatments.
Here’s a traditional Mediterranean dish from the island of Crete that uses one cup of extra virgin olive oil.
2. Dark Chocolate
Like olive oil, processing of dark chocolate started over 2000 years ago. Dark chocolate contains flavonoids that have been associated with lowering blood pressure and its main ingredient cocoa is connected with lowered risk of heart disease.

Cocoa beans are grown in tropical regions and usually harvested by hand. After the beans are released from their pods, they go through a process of fermentation that brings out the more subtle flavors in the beans. Next, the beans are roasted and then milled into cocoa powder, cocoa butter and chocolate liquor. Different combinations of these ingredients and others creates the variety of chocolate products we are familiar with such as dark chocolate, milk chocolate and white chocolate.
3. Yogurt
Yogurt is high in healthy fat and an excellent source of probiotics. The Mediterranean Diet is high in fat, which means that the food fills you up as opposed to other diets that leave you feeling hungry all the time. Yogurt also contains healthy bacteria that will aid your body in digestion and boost your metabolism. Over time, this will result in a healthy microbiome.

Here’s a recipe for homemade yogurt!
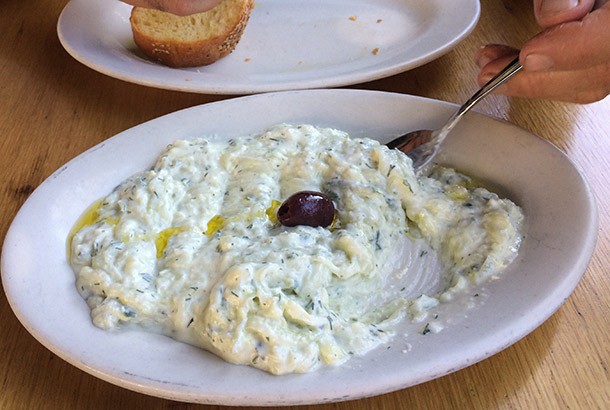

Try out this recipe for Loaded Tzatziki Yogurt Sauce with Fresh Dill, Garlic and Cucumber
4. Nut Butters
Like yogurt, nut butters are high in healthy unsaturated fats. They are also packed with nutrients like Vitamin B6, folic acid, magnesium, copper and potassium. Picking the right brand and reading the labels of the nut butters you choose is essential in finding a product that is free of preservatives and refined sugars.

The original nut butter was peanut butter and for that reason the processing of other types of nut butters including almond, cashew, macadamias and seed butters is predominantly the same. Peanut plants are harvested in the fall and then the nuts are roasted in revolving ovens. They are then ground up and mixed. At this point some brands will add things like high fructose corn syrup while others will skip these additions. Again, it is important to buy nut butters that contain little to no added ingredients.
5. Fermented Foods
Fermented foods owe their abundance of probiotics to the fermentation process. Fermentation is central in the creation of wine, beer, pickles, kimchi, yogurt and more. You can now ferment food at home fairly easily. Fermented vegetables such as cucumbers, cabbage (sauerkraut), radishes and beets are all fair game! Nurture your microbiome and start boosting your metabolism and easing your digestion.
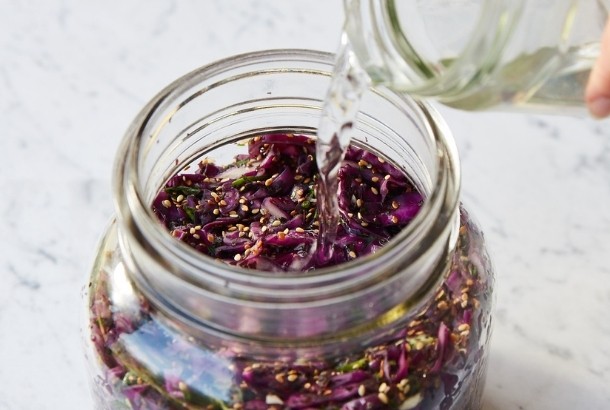

Learn more how to ferment your own foods here.
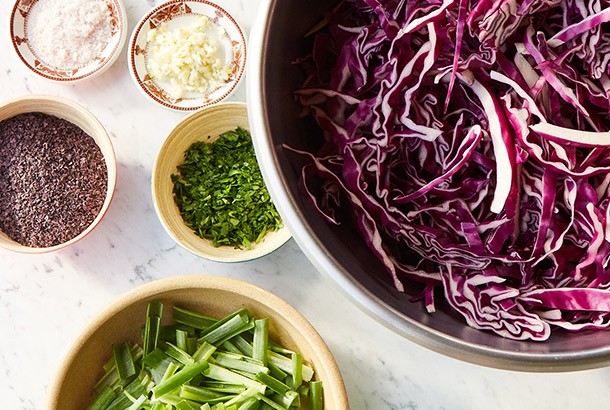

Try out this tasty recipe for Deep-Sea Purple Kraut
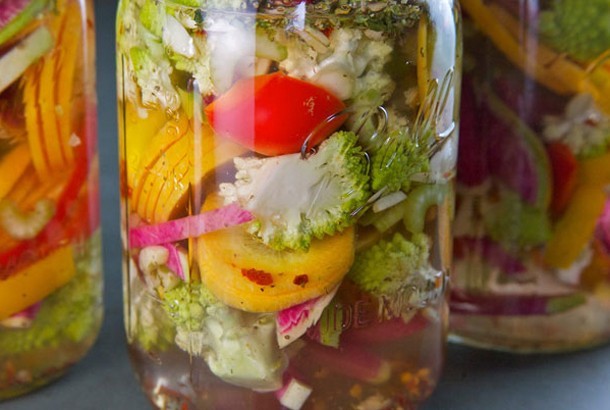
Want more probiotics? Check out this recipe for Italian Giardiniera
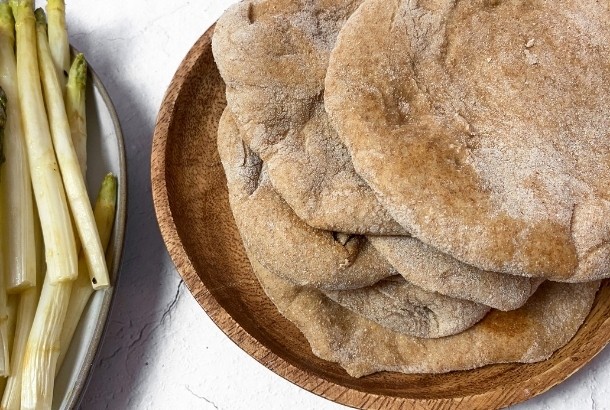
6. Bread
Bread is a food that is not commonly thought of as “processed”. Different types of bread undergo more processing than others and the nutritional value of bread definitely varies. Highly processed grains have been shown to lead to type 2 diabetes. Less processed grains are high in fiber and contain more complex carbohydrates that maximize the amount of energy we receive. An easy way to consume more of these types of grains is by buying whole grain bread or baking with organic, unbleached wheat flour. Bread is considered “whole grain” when it contains all three grain types – bran, germ and endosperm.
Try out this recipe for Whole Wheat Pita Bread

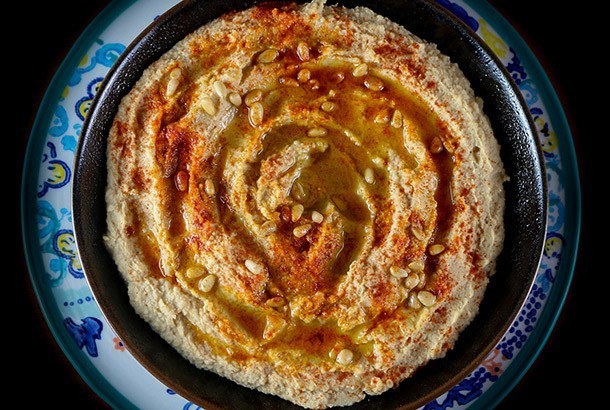
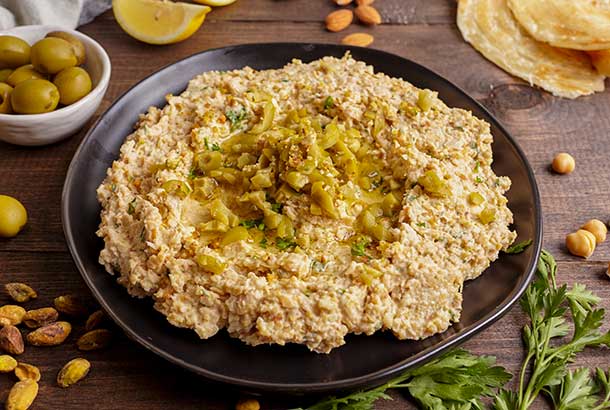
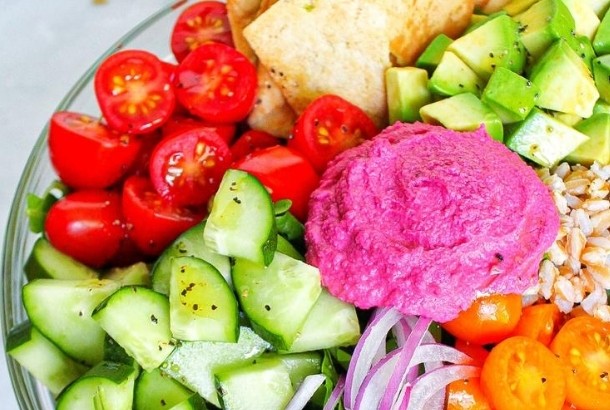
7. Hummus
Whether it’s a hummus recipe from Lebanon, a 14th century Egyptian hummus or a more modern beet hummus, hummus is one of our favorites as well as a favorite of many other proponents of the Mediterranean Diet. Why is hummus so highly favored? Well, hummus is rich in protein and dietary fiber thanks to its main ingredient chickpeas but it is also anti-inflammatory and high in healthy fats because of the garlic, lemon, tahini and extra virgin olive oil.
Check out the three different hummus recipes we have up on our site:















Bill Bradley, R.D. says:
Bill Bradley, R.D. says:
Bill Bradley, R.D. says: